Part:BBa_K1080010
YCF54
Usage and Biology
The structure of the chlorophyll molecule is the isocyclic ring. The formation of the ring is dependent by the action of enzyme Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (oxidative) cyclase. The catalysis of this enzyme to divinyl protochlorophyllide.
Essential for the formation of protochlorophyllide is the catalysis of Protoporphyrin Monomethylester Oxidative Cyclase. This is achieved by the interaction YCF 54 with other components integral in the formation, XanL or CTH1 and plastocyanin. The activity and stability of the Protoporphyrin Monomethylester Oxidative Cyclase is dependent on the YCF54 component when forming protochlorophyllide.
Operon Usage
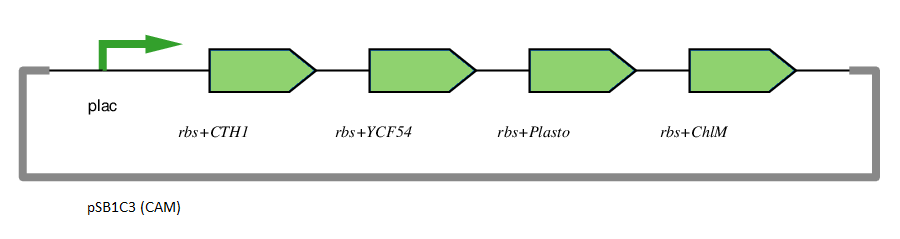
This gene has been used in an operon with other genes responsible for catalysing the biosynthesis pathway from Mg-protoporphyrin IX to Protochlorophyllide. CTH1, Plastocyanin, and YCF54 are involved in the oxidative cyclase pathway. ChlM methylates Mg-protoporphyrin IX, facilitating the highly-regulated catalysis of Mg-chelatase. CTH1 catalyses the conversion of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl into divinyl protochlorophyllide, interacting with YCF54 and Plastocyanin.
The insertion of magnesium is the key component of the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway.
The plasmid is under the control of the lac promoter.
Biobrick Design:
Source Genbank accession: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NW_001843510.1?report=genbank&from=2030539&to=2032329&strand=true NW_001843510.1]
Source Uniprot reference: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/A8ILP2 A8ILP2]
cDNA gene sequence from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was sourced from NCBI database, chloroplast targeting sequence was removed. EcoRI/XbaI/SpeI/PstI restriction sites were removed via codon adjustment, biobrick prefix and RBS were added to start of gene, biobrick suffix added to end of gene.
Biobrick construction: Restriction and ligation of 1 synthesised DNA fragment into BB vector.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 108
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 270
Amino acid sequence
MAPAAASADK ATAAEYYALV CNAEWFFMDP QNESVAEQLR EKVRFFKEQN KERDFFIVPN
PKWLDAKFPE QAKQVKRPCV ALVSTDKMWI TFMKLRLDRV LKIDLKSMPA SEVLAAGEAL
PDFKPDGKWT APYARYTPGW WNVFLPNH
References and documentation are available.
Please note the modified algorithm for extinction coefficient.
Number of amino acids: 148
Molecular weight: 17073.7
Theoretical pI: 8.50
Amino acid composition:
Ala (A) 20 13.5%
Arg (R) 7 4.7%
Asn (N) 6 4.1%
Asp (D) 9 6.1%
Cys (C) 2 1.4%
Gln (Q) 5 3.4%
Glu (E) 10 6.8%
Gly (G) 3 2.0%
His (H) 1 0.7%
Ile (I) 3 2.0%
Leu (L) 11 7.4%
Lys (K) 14 9.5%
Met (M) 5 3.4%
Phe (F) 10 6.8%
Pro (P) 12 8.1%
Ser (S) 5 3.4%
Thr (T) 5 3.4%
Trp (W) 6 4.1%
Tyr (Y) 4 2.7%
Val (V) 10 6.8%
Pyl (O) 0 0.0%
Sec (U) 0 0.0%
(B) 0 0.0% (Z) 0 0.0% (X) 0 0.0%
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 19
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 21
Atomic composition:
Carbon C 785 Hydrogen H 1190 Nitrogen N 202 Oxygen O 212 Sulfur S 7
Formula: C785H1190N202O212S7 Total number of atoms: 2396
Extinction coefficients:
Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.
Ext. coefficient 39085 Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 2.289, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines
Ext. coefficient 38960
Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 2.282, assuming all Cys residues are reduced
Estimated half-life:
The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).
The estimated half-life is:
30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).
>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).
>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).
Instability index:
The instability index (II) is computed to be 35.64 This classifies the protein as stable.
Aliphatic index: 70.00
Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.385
Source
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
References
Hollingshead, S., et al. (2012). "Conserved chloroplast open-reading frame ycf54 is required for activity of the magnesium protoporphyrin monomethylester oxidative cyclase in Synechocystis PCC 6803." J Biol Chem 287(33): 27823-27833.
| None |
